El industria de la cadena de frío es la columna vertebral de la alimentación mundial, cadenas de suministro farmacéuticas y biotecnológicas. En 2025 Este sector está en auge, valorado en aproximadamente 436,30 mil millones de dólares con proyecciones superiores 1,3 billones de dólares por 2034. Disrupciones geopolíticas, El crecimiento del comercio electrónico y las regulaciones más estrictas están remodelando la forma en que se almacenan y transportan los productos sensibles a la temperatura.. En esta guía descubrirá por qué es importante la industria de la cadena de frío., cómo está evolucionando y qué puedes hacer para mantenerte a la vanguardia.
¿Por qué la industria de la cadena de frío es fundamental en 2025? Comprender su papel y sus impulsores de crecimiento, incluidos los alimentos de origen vegetal., Productos farmacéuticos y comercio mundial..
¿Qué tecnologías están transformando la logística de la cadena de frío?? Obtenga más información sobre la optimización de rutas impulsada por IA, cadena de bloques, Almacenamiento con energía solar y sensores de IoT..
¿Cómo influyen las regulaciones y la sostenibilidad en las operaciones?? Explorar FSMA 204 Comienzan las reglas de trazabilidad y las restricciones de HFC. 2025.
¿Qué tendencias de mercado y conocimientos regionales dan forma a la industria?? Descubra previsiones para los mercados globales y norteamericanos y el ascenso de las economías emergentes.
¿Cómo puedes optimizar tus operaciones?? Obtenga consejos prácticos sobre el seguimiento, capacitación, energías renovables y planificación de contingencias.
¿Cuáles son las últimas innovaciones para 2025 y más allá? Ver equipos emergentes, Nuevas categorías de productos y nuevos métodos de entrega..
¿Qué es la industria de la cadena de frío y por qué es fundamental? 2025?
Definición e importancia: La industria de la cadena de frío abarca todos los procesos y tecnologías utilizados para manejar, almacene y transporte productos sensibles a la temperatura manteniendo rangos de temperatura estrictos. Esto incluye almacenes frigoríficos., vehículos aislados y sofisticados sistemas de monitoreo. En 2025 la industria es indispensable, apoyando el suministro mundial de alimentos, vacunas, productos biológicos y alimentos de origen vegetal.
Impulsores del crecimiento: La demanda está aumentando porque los consumidores esperan productos frescos., productos seguros y los reguladores imponen estrictas normas sobre alimentos y medicamentos. La investigación estima el mercado de logística de la cadena de frío en 436,30 mil millones de dólares en 2025, proyectado para superar 1,3 billones de dólares por 2034 con un 13.46 % Tocón. Este crecimiento se ve impulsado por la expansión del comercio mundial de alimentos perecederos., el auge de las entregas de comestibles y el comercio electrónico en línea y la rápida innovación tecnológica. Las economías emergentes con ingresos crecientes y urbanización añaden más demanda.
Nuevas categorías de productos: Proteínas de origen vegetal, Los alimentos orgánicos y sin gluten se están volviendo populares. Bloomberg Intelligence predijo que los alimentos de origen vegetal podrían representar 7.7 % del mercado mundial de proteínas por 2030 con un 162 mil millones de dólares valor. Estos productos requieren servicios especializados de cadena de frío., y muchos productores son pequeñas o medianas empresas que necesitan orientación.
Auge farmacéutico y biológico: Biofarmacéuticos, Las vacunas de ARNm y las terapias genéticas exigen temperaturas ultrabajas. Global Market Insights destaca que los productos biológicos y las vacunas de ARNm requieren temperaturas de almacenamiento y transporte ultrabajas, presionando a los proveedores de logística para que actualicen sus equipos. Como aproximadamente 20 % de nuevas drogas en desarrollo se encuentran terapias genéticas y celulares, La capacidad de logística ultrafría se está convirtiendo en una necesidad competitiva..
Desafíos operativos: Infraestructura envejecida, Las ineficiencias y la presión regulatoria obligan a las empresas a modernizar las instalaciones.. Muchos edificios de almacenamiento en frío tienen entre 40 y 50 años y requieren mejoras en la automatización., sostenibilidad y visibilidad. Al mismo tiempo, Altos costos operativos y energéticos., La escasez de mano de obra y las variaciones de temperatura amenazan la rentabilidad..
Componentes de una cadena de frío moderna
Sistemas de refrigeración: Compresores, Los condensadores y evaporadores reducen las temperaturas del producto al rango apropiado., Garantizar que los productos se mantengan dentro de los umbrales especificados..
Almacenamiento con temperatura controlada: Los almacenes frigoríficos utilizan paneles aislantes, sistemas automatizados de almacenamiento y recuperación y estanterías para paletas de alta densidad para minimizar las fluctuaciones de temperatura.
Infraestructura de transporte: Camiones aislados, contenedores frigoríficos, Los vagones refrigerados y los congeladores criogénicos portátiles mantienen la temperatura durante el tránsito.. Algunas instalaciones utilizan unidades criogénicas móviles capaces de mantener entre –80 °C y –150 °C para productos biológicos..
Sistemas de seguimiento y control.: Los sensores y registradores de datos de IoT transmiten la temperatura en tiempo real, datos de humedad y ubicación, permitiendo una acción inmediata si las condiciones se desvían.
Protocolos de aseguramiento de la calidad.: Mapeo de temperatura, planes de respuesta a emergencias y primero en entrar, primero en salir (FIFO) La gestión de inventario garantiza el cumplimiento y minimiza el desperdicio..
Rangos de temperatura típicos
| Rango de temperatura | Objetivo | Productos de ejemplo | Lo que significa para ti |
| Ambiente (59–86 °F) | Temperatura ambiente controlada para mercancías no perecederas o de bajo riesgo. | alimentos secos, algunos productos farmaceuticos | Costos mínimos de refrigeración.; Asegúrese de que haya una ventilación adecuada para evitar la acumulación de calor. |
| Fresco (50–59 °F) | Enfriamiento suave para preservar el sabor y la textura. | Queso, productos frescos | Reduce el deterioro; requiere contenedores aislados y tiempos de transporte cortos |
| Refrigerado (32–50 °F) | Previene el crecimiento bacteriano y mantiene la frescura. | Vacunas, productos lácteos | Control estricto de la temperatura; Utilice sensores de IoT para monitoreo en tiempo real |
| Congelado (–22–32 °F) | Conservación a largo plazo de productos perecederos. | Carne, mariscos, postres congelados | Requiere equipos de ultracongelación y planes de redundancia para fallas eléctricas. |
Consejos prácticos y recomendaciones
Plan de contingencias: Desarrollar protocolos de respuesta de emergencia para fallas de equipos o cortes de energía para evitar daños..
Utilice sensores de IoT: Instale sensores inteligentes en unidades de almacenamiento y vehículos para rastrear la temperatura y la humedad y automatizar alertas cuando se superen los umbrales..
Entrena a tu equipo: Educar periódicamente al personal sobre los procedimientos de manipulación., registro de datos y respuestas de emergencia para mantener la integridad del producto.
Ejemplo del mundo real: En 2024 CJ Logistics America anunció una instalación de almacenamiento en frío cerca de Kansas City con sistemas automatizados, Refrigeración energéticamente eficiente y monitoreo de IoT: lo que demuestra cómo el almacenamiento en frío moderno combina tecnología y sostenibilidad..
¿Qué tecnologías están transformando la logística de la cadena de frío? 2025?
Optimización de rutas impulsada por IA y análisis predictivo
Inteligencia artificial (AI) analiza datos históricos y en tiempo real para predecir fallas de equipos, optimizar las rutas de entrega y pronosticar la demanda. Los algoritmos de IA calculan las rutas más eficientes considerando el tráfico, ventanas meteorológicas y de entrega, Reducir el consumo de combustible y garantizar que los productos se mantengan dentro de las especificaciones de temperatura.. El mantenimiento predictivo utiliza datos de sensores para anticipar fallas en las unidades de refrigeración, permitiendo reparaciones proactivas y reduciendo el tiempo de inactividad. Modelos de previsión de la demanda patrones de consumo estacionales, Ayudar a las empresas a ajustar el inventario y reducir el desperdicio..
Monitoreo en tiempo real habilitado para IoT
El internet de las cosas (IoT) se refiere a una red de dispositivos conectados, como sensores inteligentes, Rastreadores GPS y registradores de datos: que recopilan y comparten datos en tiempo real. Los dispositivos IoT brindan visibilidad de extremo a extremo en toda la cadena de frío, temperatura de transmisión, Información de humedad y ubicación a plataformas centrales.. Los beneficios incluyen la prevención del deterioro mediante un monitoreo continuo., Garantizar el cumplimiento normativo proporcionando registros verificables., y generar confianza en el cliente compartiendo datos en vivo. En 2022 el segmento de hardware para el seguimiento de la cadena de frío retenido 76 % de cuota de mercado, destacando la rápida adopción de estos dispositivos.
Blockchain para una trazabilidad mejorada
La tecnología Blockchain crea registros a prueba de manipulaciones de los recorridos de los productos, permitiendo la trazabilidad de extremo a extremo y mejorando la transparencia. Por ejemplo, Las compañías farmacéuticas pueden registrar datos de temperatura y ubicación en un libro de contabilidad blockchain., permitiendo a los fabricantes, transportadores y clínicas para acceder al mismo registro inmutable. Esto reduce el riesgo de manipulación de datos., simplifica las auditorías y respalda el cumplimiento de FSMA 204 requisitos de trazabilidad. El valor de Blockchain se extiende más allá de los productos farmacéuticos: genera confianza en el consumidor y ayuda a las marcas a demostrar su autenticidad.
Refrigeración con energía solar e innovaciones sostenibles
El consumo de energía es un importante factor de costes en la cadena de frío.. Las unidades de refrigeración alimentadas por energía solar, especialmente en regiones rurales o con escasez de energía, utilizan paneles solares para alimentar el almacenamiento en frío., reducir la dependencia de la electricidad de la red. En los Estados Unidos, Las tarifas de electricidad solar comercial varían desde 3.2 a 15.5 centavos por kWh, ofreciendo ahorros potenciales en comparación con las tarifas promedio de servicios públicos. Otras innovaciones incluyen congeladores criogénicos portátiles capaces de mantener temperaturas ultrabajas para productos biológicos., Contenedores de envío inteligentes y livianos con sensores de IoT y soluciones de embalaje sostenibles, como envoltorios biodegradables y compresas frías reutilizables..
El papel de la IA, IoT, Blockchain y energía solar en su negocio
| Innovación | Descripción | Beneficios prácticos |
| Optimización de rutas impulsada por IA | Los algoritmos analizan el tráfico., Clima y horarios de entrega para encontrar rutas eficientes.. | Entregas más rápidas, menores costos de combustible y menor deterioro. |
| Mantenimiento predictivo & analítica | La IA predice fallas en los equipos y tendencias de la demanda. | Menos tiempo de inactividad y mayor satisfacción del cliente. |
| Sensores IoT y seguimiento en tiempo real | Los dispositivos monitorean la temperatura, humedad y ubicación. | Alertas inmediatas, Menos pérdidas de productos y mayor cumplimiento normativo.. |
| Trazabilidad de la cadena de bloques | Los registros del libro mayor distribuido garantizan datos a prueba de manipulaciones. | Mayor transparencia, Reducción del fraude y auditorías simplificadas.. |
| Refrigeración con energía solar | Paneles solares alimentan unidades de almacenamiento en frío. | Menores costos de energía y reducción de la huella de carbono.. |
| Congeladores criogénicos portátiles | Las unidades móviles mantienen de –80 °C a –150 °C. | Permite la distribución flexible de productos biológicos y terapias celulares ultrafríos.. |
| Embalaje sostenible | Los envases reciclables y los envoltorios biodegradables reducen los residuos. | Apoya los objetivos de sostenibilidad corporativa y el cumplimiento normativo.. |
Ejemplos y estudios de casos del mundo real
Estudio de caso: Blockchain en el sudeste asiático: Las cadenas de suministro farmacéuticas del sudeste asiático utilizan sistemas de seguimiento basados en blockchain para registrar la temperatura, humedad y tiempo de viaje en un libro mayor distribuido. Los datos en tiempo real brindan a las partes interesadas un acceso seguro y garantizan el cumplimiento, mientras que el almacenamiento con energía solar y los sensores de IoT protegen los medicamentos.
Lanzamientos de nuevos equipos: Global Market Insights informa que el mercado de equipos de logística de cadena de frío crecerá de 94.300 millones de dólares en 2025 a 179.800 millones de dólares 2034 con un 7.4 % Tocón. Los fabricantes están diseñando refrigeración más eficiente energéticamente, Equipos de manipulación automatizados y sistemas de seguimiento rápido para mantener la calidad.. Empresas como Carrier Transicold y Thermo King están adoptando unidades de refrigeración eléctricas e híbridas para reducir las emisiones..
¿Cómo influyen las regulaciones y la sostenibilidad en la industria de la cadena de frío??
FSMA 204 Requisitos de trazabilidad
En Enero 6 2025, el Ley de modernización de la seguridad alimentaria (FSMA) sección 204 entró en vigor para los alimentos incluidos en la Lista de trazabilidad de alimentos de la FDA. Entidades que fabrican, proceso, empacar o almacenar estos alimentos debe registrar elementos de datos clave para cada evento de seguimiento crítico para garantizar una trazabilidad rápida. El cumplimiento exige que las empresas proporcionen estos registros a la FDA dentro de 24 horas, Impulsar la inversión en mantenimiento de registros digitales y monitoreo en tiempo real..
Restricciones de HFC y regulaciones de sostenibilidad
Las regulaciones también están empujando a los operadores hacia refrigerantes amigables con el medio ambiente.. Comienzo Enero 1 2025, Es posible que ciertas tecnologías ya no utilicen hidrofluorocarbonos con alto potencial de calentamiento global. (HFC) o mezclas de HFC. Se aplican prohibiciones a la fabricación., distribución, venta, instalación y exportación de productos que contienen HFC restringidos. Estas restricciones aceleran la transición a refrigerantes naturales y sistemas energéticamente eficientes y, a menudo, van acompañadas de incentivos fiscales o sanciones por incumplimiento..
Modernización de la infraestructura antigua
Muchas instalaciones de almacenamiento en frío construidas hace 40 a 50 años son ineficientes y requieren actualizaciones para mejorar la automatización., sostenibilidad y visibilidad. Los operadores están reemplazando o modernizando edificios antiguos con sistemas automatizados de almacenamiento y recuperación., aislamiento de alta eficiencia y monitoreo habilitado para IoT. Normas más estrictas sobre refrigerantes sintéticos (HCFC y HFC) y el aumento de los costos de la energía son factores clave para esta modernización.
La sostenibilidad como ventaja competitiva
Inversores y clientes evalúan cada vez más a los operadores de la cadena de frío en función de su desempeño ambiental. Las iniciativas de sostenibilidad incluyen:
Refrigerantes naturales: Usando amoníaco (NH₃), dióxido de carbono (Co₂) o hidrocarburos, que tienen un menor potencial de calentamiento global que los HFC.
Eficiencia energética: Adopción de compresores de alta eficiencia, Los variadores de velocidad y el aislamiento térmico reducen el consumo de energía.. La refrigeración con energía solar es particularmente atractiva en regiones con altos costos de electricidad..
Embalaje ecológico: Los materiales de embalaje biodegradables o reciclables reducen los residuos y se alinean con las expectativas de los consumidores..
Normas de construcción ecológica: Las instalaciones de almacenamiento en frío con certificación LEED utilizan iluminación natural, Sistemas HVAC energéticamente eficientes y materiales sostenibles para minimizar el impacto ambiental..
Las regulaciones crean oportunidades
Cumplimiento de la FSMA 204 y las restricciones a los HFC pueden parecer onerosas, pero también abre nuevas oportunidades de negocio. Empresas que invierten en tecnologías de trazabilidad, La energía renovable y la refrigeración sostenible pueden diferenciarse, asegurar clientes premium y evitar multas. Incentivos regulatorios, como créditos fiscales por eficiencia energética y refrigerantes de bajo PCA, compensar los costos de inversión inicial.
¿Cuáles son las tendencias clave del mercado y la información regional para la logística de la cadena de frío??
Tendencias del mercado global
Las agencias de investigación de mercado proyectan un fuerte crecimiento en todos los segmentos de la industria de la cadena de frío. Precedence Research informa que el mercado global de logística de cadena de frío crecerá de 436,30 mil millones de dólares en 2025 a 1,359 billones de dólares estadounidenses 2034, a 13.46 % Tocón. Los controladores incluyen:
Expansión del comercio mundial de alimentos: Mayor demanda de productos frescos y mariscos, junto con cadenas de suministro interconectadas, impulsa la inversión.
Auge del comercio electrónico: Los servicios de compra de comestibles en línea y entrega de kits de comida requieren redes de entrega confiables con temperatura controlada.
Crecimiento farmacéutico y biológico: La creciente demanda de vacunas y medicamentos personalizados impulsa las inversiones en almacenamiento ultrafrío.
Requisitos reglamentarios: Las regulaciones de seguridad alimentaria como FSMA y estándares similares en todo el mundo exigen un estricto control y documentación de la temperatura..
Presiones de sostenibilidad: La conciencia medioambiental empuja a las empresas a adoptar tecnologías energéticamente eficientes y envases ecológicos.
Perspectivas regionales
Asia-Pacífico: Urbanización rápida, El aumento de los ingresos y el crecimiento de las clases medias impulsan el crecimiento de la cadena de frío de la región.. MarketsandMarkets proyecta que la industria global de la cadena de frío alcanzará 372 mil millones de dólares por 2029, con Asia-Pacífico a la cabeza debido a la fuerte demanda de venta minorista organizada y alimentos procesados. El alto consumo de lácteos en la India (427 g per cápita versus un promedio global de 305 gramo) y el auge de los restaurantes de servicio rápido (proyectado 20-25 % crecimiento en el año fiscal 2024) subrayar la urgente necesidad de una logística fiable.
América del norte: El mercado de la cadena de frío de América del Norte alcanzó 116.850 millones de dólares en 2024 y se prevé que crezca a un 9.50 % Tocón entre 2025 y 2034, alcance 289,58 mil millones de dólares. El mercado maduro pero en expansión de la región está impulsado por la demanda biofarmacéutica, Crecimiento del comercio electrónico e inversiones en nuevas instalaciones de almacenamiento y transporte transfronterizo.. Los operadores están adoptando prácticas sostenibles, Equipos energéticamente eficientes y sistemas de monitoreo avanzados..
Europa: La conciencia medioambiental y las estrictas regulaciones empujan a los operadores europeos a adoptar tecnologías respetuosas con el medio ambiente y prácticas energéticamente eficientes.. La infraestructura antigua se está modernizando para cumplir con los estándares actuales de eficiencia y sostenibilidad..
Mercados emergentes: Países del sudeste asiático, África y América Latina invierten fuertemente en capacidad de cadena de frío para respaldar los crecientes mercados de consumo y las necesidades farmacéuticas.. La refrigeración con energía solar y la trazabilidad de blockchain son especialmente valiosas en regiones con energía poco confiable o desafíos regulatorios..
Segmentación del mercado y oportunidades
El mercado de la cadena de frío se puede segmentar por tipo de servicio (transporte, servicios de almacenamiento y valor agregado), rango de temperatura (ambiente, Frío, refrigerado, congelado), tecnología (vehículos frigoríficos, Soluciones de IoT, automatización) y uso final (comida y bebida, productos farmaceuticos, biotecnología). Por ejemplo:
Tecnología de hielo seco capturado 55.16 % de cuota de mercado en 2024, mientras almacenes frigoríficos representado 238.290 millones de dólares.
Instalaciones de preenfriamiento de Asia y el Pacífico generado 204.400 millones de dólares en ingresos en 2024, destacando la importancia del enfriamiento temprano de frutas y verduras.
Segmentación del tipo de servicio: El mercado de la cadena de frío de América del Norte se divide entre almacenamiento refrigerado y transporte refrigerado., con inversiones en almacenamiento centradas en la automatización y la sostenibilidad.
Segmentación de uso final: Productos farmacéuticos, carnes y mariscos, Los productos lácteos y congelados son los principales contribuyentes..
Desarrollos notables de la industria (2024–2025)
Ampliaciones de instalaciones: Los operadores norteamericanos están invirtiendo en nuevas instalaciones de almacenamiento y transporte transfronterizo.. CJ Logistics America planea una instalación de almacenamiento en frío cerca de Kansas City. Lineage Logistics está introduciendo servicios de transporte transfronterizo que unen los EE. UU. y Canadá. Agile Cold Storage está invirtiendo 45,9 millones de dólares en una instalación de almacenamiento en frío automatizada en Luisiana. United States Cold Storage está ampliando su almacén en Tulare North 8.56 millones de pies cúbicos.
Avances tecnológicos: Los fabricantes lanzan al mercado nuevas unidades frigoríficas de transporte eléctricas e híbridas. Por ejemplo, Thermo King presentó las unidades totalmente eléctricas A 500e y híbrida S 750i en 2025, mientras que Carrier Transicold presentó el Vector S 15 unidad de remolque con tecnología totalmente eléctrica.
Iniciativas de sostenibilidad: Las empresas están invirtiendo en refrigerantes naturales, Compresores energéticamente eficientes y energías renovables.. Daikin Industries y Carrier Transicold destacan los compresores energéticamente eficientes y la tecnología E Drive para cumplir con los requisitos reglamentarios y la demanda de los clientes..
¿Cómo pueden las empresas optimizar sus operaciones de cadena de frío en 2025?
Desarrollar un monitoreo y control sólidos
Implemente sensores de IoT y registradores de datos automatizados en unidades de almacenamiento y vehículos para monitorear la temperatura., humedad y ubicación en tiempo real. Los paneles centralizados pueden analizar estos datos y activar alertas cuando las condiciones se desvían. El monitoreo continuo ayuda a prevenir el deterioro y garantiza el cumplimiento de la FSMA y las regulaciones farmacéuticas..
Plan de Contingencias y Resiliencia
Las fallas en la cadena de frío ocurren a menudo debido a cortes de energía, averías de equipos o alteraciones climáticas. Crear planes de contingencia que incluyan suministros de energía redundantes. (como generadores y baterías de respaldo), protocolos de respuesta a emergencias y programas de mantenimiento proactivos. Las pruebas de estrés y los simulacros periódicos garantizan que su equipo pueda responder rápidamente cuando se produzcan interrupciones..
Invertir en formación y cultura del personal
El error humano contribuye a muchas variaciones de temperatura.. Llevar a cabo capacitaciones periódicas sobre los procedimientos de manipulación., registro de datos y respuesta de emergencia. Fomentar una cultura de mejora continua fomentando la retroalimentación y compartiendo las mejores prácticas entre departamentos.. Una fuerza laboral capacitada mejora el cumplimiento y la satisfacción del cliente.
Evaluar energías renovables y envases sostenibles
Evaluar la viabilidad de instalar paneles solares en techos de almacenes y camiones frigoríficos. Compare los ahorros a largo plazo y los incentivos fiscales disponibles con los costos iniciales. Incorporar envases biodegradables o reciclables para reducir los residuos y alinearse con las expectativas de los consumidores..
Integre la IA y el análisis de datos
Adopte herramientas de inteligencia artificial para optimizar rutas, pronosticar la demanda y predecir fallas en los equipos. Integre estos sistemas con experiencia humana, utilizando la IA como herramienta de apoyo a la toma de decisiones y al mismo tiempo reteniendo personal experimentado para adaptarse a condiciones imprevistas.. Comience con proyectos piloto para evaluar los beneficios antes de escalar.
Colabore con socios experimentados
Las pequeñas y medianas empresas que entran en la industria de la cadena de frío a menudo carecen de experiencia en logística.. Asóciese con proveedores experimentados que tengan redes extensas, Infraestructura tecnológica y conocimiento regulatorio para garantizar el transporte seguro y eficiente de mercancías sensibles a la temperatura.. La colaboración reduce el riesgo, mejora la visibilidad y ayuda a escalar las operaciones a medida que crece la demanda.
¿Cuáles son los últimos desarrollos e innovaciones que se esperan en 2025 y más allá?
Productos y equipos emergentes
Se prevé que el mercado mundial de equipos de logística de cadena de frío crezca de 94.300 millones de dólares en 2025 a 179.800 millones de dólares 2034. Las innovaciones incluyen:
Todas las unidades de refrigeración eléctricas e híbridas.: Empresas como Thermo King y Carrier Transicold están lanzando unidades de refrigeración de transporte eléctricas e híbridas para reducir el uso de combustible y las emisiones.. Las unidades A 500e y S 750i híbridas ofrecen prestaciones de larga distancia sin diésel, mientras que el Vector S del transportista 15 utiliza tecnología totalmente eléctrica E Drive.
Herramienta digital Scout AI: Emerson Electric presentó Scout AI en septiembre de 2025, una herramienta digital que proporciona diagnósticos en tiempo real, Mantenimiento predictivo y monitoreo remoto para equipos de cadena de frío.. Estas soluciones mejoran la confiabilidad y reducen los costos de mantenimiento..
Contenedores inteligentes y congeladores criogénicos portátiles: Contenedores aislados livianos equipados con sensores IoT monitorean la temperatura, humedad y ubicación. Los congeladores criogénicos portátiles mantienen temperaturas ultrafrías para productos biológicos y terapias celulares.
Materiales de embalaje sostenibles: Las empresas están desarrollando envases ecológicos, como envoltorios térmicos biodegradables y compresas frías reutilizables.. Estos materiales minimizan el impacto ambiental y cumplen con los requisitos reglamentarios..
Nuevos modelos de servicio y estrategias de distribución
Microalmacenes distribuidos: Reducir los tiempos de tránsito y mejorar la entrega de última milla, Algunos operadores están estableciendo instalaciones regionales más pequeñas y más cercanas a los consumidores.. Esto mejora la flexibilidad y reduce el riesgo de variaciones de temperatura durante la entrega final..
Planificación inteligente de rutas: El software impulsado por IA integra datos de tráfico, patrones climáticos y ventanas de entrega para generar rutas dinámicas, mejorar la eficiencia y la resiliencia.
Almacenamiento en frío bajo demanda: Las unidades modulares portátiles brindan almacenamiento temporal para picos estacionales o ubicaciones remotas. Permiten a las empresas ampliar su capacidad sin grandes gastos de capital..
Mercados emergentes y categorías de productos
Alimentos de origen vegetal: La creciente popularidad de las alternativas basadas en plantas está impulsando la demanda de logística especializada en la cadena de frío.. Los pequeños y medianos productores requieren de una infraestructura sólida para mantener la calidad.
Innovación farmacéutica: Terapias genéticas y celulares., Los productos biológicos y la medicina personalizada requieren capacidades logísticas ultrafrías.. Los congeladores criogénicos portátiles y la trazabilidad habilitada por blockchain garantizan la integridad del producto y el cumplimiento normativo..
Expansión del comercio mundial: Los gobiernos están lanzando programas de exportación, por ejemplo, El Programa de Exportación de Lácteos del Reino Unido—para impulsar las exportaciones de lácteos por valor de más de 2.470 millones de dólares anualmente a 135 países. Estos programas impulsan la demanda de soluciones avanzadas de cadena de frío..
2025 Últimas tendencias y desarrollos
Panorama general de las tendencias tecnológicas y del mercado
La industria de la cadena de frío en 2025 se define por un alto crecimiento y una rápida innovación. Los mercados se están expandiendo en todo el mundo.; Se prevé que el valor del mercado mundial supere 1 billón de dólares dentro de la década. Crecimiento del comercio electrónico, El comercio mundial de alimentos y la demanda farmacéutica están intensificando la presión sobre los proveedores de logística para realizar entregas a escala y con precisión.. Mandatos regulatorios, como FSMA 204 y eliminación de HFC, están acelerando la adopción de la trazabilidad digital y la refrigeración sostenible.
Últimos desarrollos de un vistazo
Influencias geopolíticas: Los disturbios geopolíticos han afectado los tiempos de tránsito y la disponibilidad de capacidad., provocando efectos en cadena sobre los niveles de existencias en algunas regiones. La industria de la cadena de frío está ganando resiliencia para hacer frente a las interrupciones.
Inversiones de visibilidad: 2025 Veremos inversiones continuas en software que mejoran la visibilidad de un extremo a otro.. Los datos ininterrumpidos son esenciales para hacer frente a las interrupciones y para un seguimiento sencillo de la ubicación y la monitorización de la temperatura..
Actualizaciones de infraestructura: Se están reemplazando o modernizando las antiguas instalaciones de almacenamiento en frío, adoptando la automatización, sostenibilidad y mejor visibilidad.
Estrategias de distribución: Las instalaciones se están ubicando más cerca de las áreas de producción o de los puertos., permitiendo una mejor integración y mayores capacidades.
Crecimiento del mercado: El mercado mundial de logística de cadena de frío se valoró en 293.580 millones de dólares en 2023 y se prevé que alcance 324.850 millones de dólares en 2024, con una previsión de 862,33 mil millones de dólares por 2032 (13 % Tocón). Se espera que el sector farmacéutico alcance 1,454 billones de dólares por 2029, enfatizando la necesidad de una logística de frío confiable.
Ideas del mercado
Los consumidores exigen cada vez más transparencia y sostenibilidad. Las redes sociales exponen a los consumidores a nuevas cocinas e influyen en los patrones de consumo.. El cumplimiento normativo no es negociable, con FSMA 204 requerir registros detallados para los alimentos en la lista de trazabilidad y la eliminación gradual de HFC empuja a los operadores hacia refrigerantes de bajo PCA. Inversión en tecnología: IA, IoT, blockchain: mejora la eficiencia y reduce el riesgo. Los mercados emergentes y los pequeños productores necesitan asociaciones con proveedores de logística experimentados para afrontar la complejidad..
Preguntas frecuentes
Q1: ¿Qué es la industria de la cadena de frío y por qué es importante??
La industria de la cadena de frío comprende procesos y tecnología que manejan, almacenar y transportar productos sensibles a la temperatura, manteniendo estrictos rangos de temperatura desde la producción hasta el consumo. Es crucial porque preserva la calidad y seguridad de productos perecederos como los alimentos., productos farmaceuticos y biologicos, prevenir el deterioro y garantizar el cumplimiento.
Q2: ¿Qué tamaño tiene el mercado de la cadena de frío en 2025?
La investigación muestra que el mercado global de logística de la cadena de frío está valorado en 436,30 mil millones de dólares en 2025 y se prevé que supere 1,3 billones de dólares por 2034, con un 13.46 % Tocón. Se espera que sólo América del Norte crezca desde 116.850 millones de dólares en 2024 a 289.580 millones de dólares por 2034, logrando un 9.50 % Tocón.
Q3: Qué tecnologías están revolucionando la logística de la cadena de frío?
Optimización de rutas impulsada por IA, mantenimiento predictivo, Sensores IoT para monitoreo en tiempo real, La trazabilidad blockchain y la refrigeración con energía solar están transformando la logística de la cadena de frío.. Estas tecnologías aumentan la eficiencia, reducir el consumo de combustible, prevenir el deterioro y mejorar el cumplimiento normativo.
Q4: ¿Qué regulaciones afectan las operaciones de la cadena de frío en 2025?
FSMA 204 exige que las empresas que manipulan alimentos incluidos en la Lista de trazabilidad de alimentos de la FDA registren elementos de datos clave para eventos de seguimiento críticos a partir de enero 6 2025. Restricciones de HFC a partir de enero 1 2025 prohibir que determinadas tecnologías utilicen refrigerantes con alto PCA.
Q5: ¿Cómo pueden las empresas mejorar sus operaciones de cadena de frío??
Implementar sensores de IoT y análisis de IA, invertir en formación de personal, Desarrollar planes de contingencia y explorar energías renovables como paneles solares.. Asóciese con proveedores experimentados de la cadena de frío para aprovechar las redes y la experiencia.
Conclusión y recomendaciones
El industria de la cadena de frío está experimentando una rápida transformación impulsada por el aumento de la demanda, innovación tecnológica y cambio regulatorio. Las previsiones del mercado predicen un crecimiento de más de 1 billón de dólares dentro de la próxima década. Para seguir siendo competitivo, Las empresas deben invertir en infraestructura moderna., Adopte IA e IoT para visibilidad y análisis predictivo, Cumplir con las regulaciones en evolución y adoptar la sostenibilidad.. Asociación con proveedores experimentados, capacitar al personal y planificar contingencias mejorará la resiliencia y la satisfacción del cliente. Ahora es el momento de auditar tus operaciones, actualice las instalaciones obsoletas e integre la trazabilidad digital para garantizar que cumpla con las expectativas de 2025 y más allá.
Acerca de Tempk
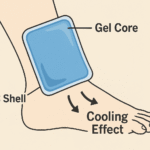
Somos Templ, un proveedor de soluciones de embalaje aislado y servicios de cadena de frío. Nuestros productos incluyen bolsas de hielo en gel., Cajas isotérmicas y bolsas térmicas reutilizables que mantienen tus mercancías dentro de rangos óptimos de temperatura.. Priorizamos la innovación: ofrecemos materiales ecológicos y sistemas habilitados para IoT para mejorar la visibilidad.. Trabajamos en estrecha colaboración con los productores de alimentos., empresas farmacéuticas y proveedores de logística para diseñar soluciones adaptadas a sus necesidades específicas.
Próximos pasos viables:
Para obtener más información sobre cómo Tempk puede respaldar sus operaciones de cadena de frío, Explore nuestras soluciones para la entrega de alimentos., Envío de productos farmacéuticos y embalaje personalizado de cadena de frío.. Para orientación personalizada, Comuníquese con nuestro equipo para analizar cómo podemos ayudarlo a optimizar su cadena de suministro con temperatura controlada..